Michigan Antibiotic Resistance Reduction Coalition
Ferris State University College of Pharmacy
25 Michigan St NE Room 706, Grand Rapids, MI 49503
[email protected]
Follow us on Facebook and Bluesky
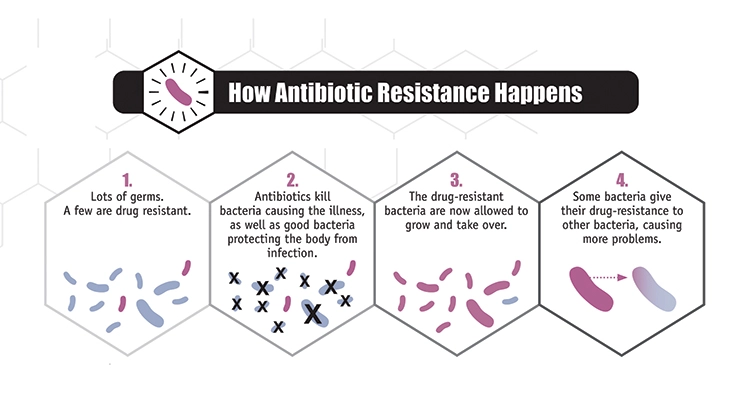
How does resistance happen?
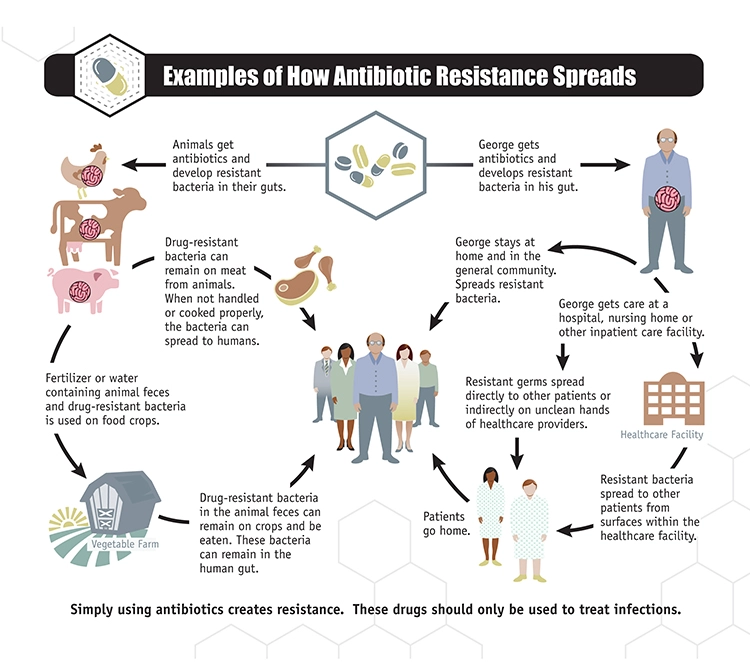
The use of antibiotics is the single most important factor leading to antibiotic resistance around the world. Simply using antibiotics creates resistance. These drugs should only be used to manage infections.
Antibiotic resistance is a growing global problem. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics are the main driving force behind this threat.
Antibiotic / Antimicrobial resistance is the ability of microbes to resist the effects of drugs and continue to grow stronger. Although people are at greater risk than others to antibiotic-resistance, no one can completely avoid the risk of antibiotic-resistant infections. Infections with resistant organisms are difficult to treat, requiring costly and sometimes toxic alternatives.
Bacteria will inevitably find ways of resisting the antibiotics developed by humans, which is why aggressive action is needed now to keep new resistance from developing and to prevent the resistance that already exists from spreading.
Trends in drug resistance
- Antibiotics are among the most commonly prescribed drugs used in human medicine and
can be lifesaving drugs. However, up to 50% of the time antibiotics are not optimally
prescribed, often done so when not needed, incorrect dosing or duration.
- The germs that contaminate food can become resistant because of the use of antibiotics
in people and in food animals. For some germs, like the bacteria Salmonella and Campylobacter,
it is primarily the use of antibiotics in food animals that increases resistance.
Because of the link the between antibiotic use in food-producing animals and the occurrence
of antibiotic-resistant infections in humans, antibiotics that are medically important
to treating infections in humans should be used in food-producing animals only under
veterinary oversight and only to manage and treat infectious disease, not to promote
growth.
- The other major factor in the growth of antibiotic resistance is spread of the resistant strains of bacteria from person to person, or from the non-human sources in the environment.